Cobb County World Language Programs
Teacher Quick Links
Programs by Language
Click HERE to access the list individual language programs as well as specific language program information.

Language Programs by Level
Bilingual and Specialized Programs
The programs below are exclusive to each school. Click over each item to find additional information.
- Dual Language Immersion**
- Globalization Academy at Pope High School
- International Baccalaureate at Campbell High School
- International Spanish Academy at Walton High School
- International Spanish Language Academy at Sprayberry High School
- International Studies at North Cobb High School
Seals
Cobb County School District the following Georgia Department of Education World Language Seals:
| Georgia Seal of Biliteracy |
International Skills Diploma Seal |
* Not all programs are available at all schools, please check with your local school for details.
** The selection of target language on Dual Language Immersion programs is a local school decision based on community input.
This Education Week article talks about the academic gains of students participating in the Dual Language Immersion program at Collinswood Language Academy in North Carolina.
"At Collinswood Language Academy, a K-8 dual-language school in a working-class neighborhood in this Southern city, students produced some of the highest math achievement scores in the Charlotte-Mecklenburg school district.
And that's the case even though they learn all their math in Spanish, and take North Carolina's annual end-of-grade math exams in English."
Click HERE to access the article.
More from Education Week on Dual Language Immersion and Bilingual Education:
- Details
- Category: Dual Language Immersion
- Hits: 4274
New York City Education Department to Add or Expand 40 Dual-Language Programs
- Details
- Category: Dual Language Immersion
- Hits: 3617
This ERIC Digest publication addresses some of the initial questions parent may have about language immersion programs. It answers the following questions:
- What is a foreign language immersion program and how does it work?
- Why should I consider enrolling my child in an immersion program?
- How will learning everything in a second language affect my child’s English language and literacy development?
- Will my child become proficient in the second language? How long will that take?
- Is immersion an appropriate choice for all children?
- What can I do to support my child’s immersion experience if I don’t speak the second language?
- Details
- Category: Dual Language Immersion
- Hits: 3640
This article from the Language Magazine presents information on the increase of Dual Language Immersion programs at the national level.
- Details
- Category: Dual Language Immersion
- Hits: 3567
 This article from the Language Magazine presents the results of the Institute for Education Science Grant "The Effect of Dual-Language Immersion on Student Achievement in the Portland Public Schools". Language Magazine highlights the improvement of students' Reading skills in English while promoting proficiency in two languages.
This article from the Language Magazine presents the results of the Institute for Education Science Grant "The Effect of Dual-Language Immersion on Student Achievement in the Portland Public Schools". Language Magazine highlights the improvement of students' Reading skills in English while promoting proficiency in two languages.
- Details
- Category: Dual Language Immersion
- Hits: 3926
The Dual Language Immersion Program at Riverside Primary is highlighted during the visit of a representative of the Governor's Office to the school.
- Details
- Category: Dual Language Immersion
- Hits: 3498
 The Center for Applied Linguistics (CAL) provides genral information, resources, and profesional learning opportunity to learn about bilingual and dual language education.
The Center for Applied Linguistics (CAL) provides genral information, resources, and profesional learning opportunity to learn about bilingual and dual language education.
- Details
- Category: Dual Language Immersion
- Hits: 3507
|
COMMUNICATION – INTERPERSONAL MODE (IP) |
|||
|
MLI.IP1: The students exchange simple spoken and written information in the target language, utilizing cultural references where appropriate. |
|||
|
A. Use basic greetings, farewells, and expressions of courtesy, in both oral and written forms B. Express likes, dislikes, emotions, agreement and disagreement. C. Make simple requests. D. Ask for clarification. E. Give simple descriptions. |
F. Comprehend basic directions. G. Ask questions and provide responses based on topics such as self, family, school, etc. H. Use sequenced information, such as the alphabet, days of the week, months, seasons, and numbers 0 to 100 in context. |
||
|
MLI.IP2: The students demonstrate skills necessary to sustain brief oral and written exchanges in the target language. |
|||
|
A. Initiate, participate in, and close a brief oral or written exchange. B. Use formal and informal forms of address. |
C. Demonstrate Novice-Mid proficiency in oral and written exchanges with respect to proper pronunciation, intonation, and writing mechanics. |
||
|
|
|||
|
COMMUNICATION – INTERPRETIVE MODE (INT) |
|||
|
MLI.INT1: The students demonstrate understanding of simple spoken and written language presented through a variety of media in the target language and based on topics such as self, family, school, etc. |
|||
|
A. Identify main ideas and some details when reading and listening. B. Comprehend simple, culturally authentic announcements, messages, and advertisements. |
C. Understand simple instructions, such as classroom procedures. D. Demonstrate Novice-Mid proficiency in listening and reading comprehension. |
||
|
MLI.INT2: The students interpret verbal and non-verbal cues to understand simple spoken and written messages in the target language. |
|||
|
A. Differentiate among statements, questions and exclamations. |
B. Recognize basic gestures, body language, and intonation that clarify a message. |
||
|
|
|||
|
COMMUNICATION - PRESENTATIONAL MODE (P) |
|||
|
MLI.P1: The students present information orally and in writing that contains a variety of vocabulary, phrases, and patterns. |
|||
|
A. Present information gathered from a variety of sources such as informal conversations, class presentations, interviews, readings, and media. B. Give basic information about self and others including school, family, activities, etc. |
C. Demonstrate Novice-Mid proficiency in oral and written presentations with respect to proper pronunciation, intonation, and writing mechanics. |
||
|
MLI.P2: The students present brief, rehearsed material in the target language, such as dialogues, skits, poetry, and songs. |
|||
|
A. Demonstrate Novice-Mid proficiency in pronunciation and intonation when presenting rehearsed material. |
B. Demonstrate comprehension of rehearsed material. |
||
|
|
|||
|
CULTURAL PERSPECTIVES, PRACTICES, AND PRODUCTS (CU) |
|||
|
MLI.CU1: The students develop an awareness of perspectives, practices, and products of the cultures where the target language is spoken. |
|||
|
A. Demonstrate knowledge of contributions of target culture(s) to civilization. B. Identify commonly held viewpoints of the cultures, such as those relating to time, education, and meals. |
C. Describe customs and traditions of the cultures such as greetings, celebrations and courtesies. |
||
|
CONNECTIONS |
COMPARISONS |
COMMUNITIES |
|
|
MLI.CCC1: The students use information acquired in the study of the target language and information acquired in other subject areas to reinforce one another. |
|||
|
A. Demonstrate knowledge of geographical locations and identify major countries, cities, and geographical features of the places where the target language is spoken. B. Apply previously learned skills from other subjects, when appropriate to demonstrate knowledge in the target language (e.g. using basic math skills). |
C. Identify examples of vocabulary, phrases, proverbs, and symbols from the target language that are used in other subjects. D. Relate content from other subject areas to topics discussed in the language class, such as the influence of explorers and settlers on various regions of the United States. |
||
|
MLC.CCC2: The students demonstrate an understanding of the significance of culture through comparisons between the culture(s) studied and the students’ own culture. |
|||
|
A. Compare patterns of behavior and interaction in the students’ own culture with those of the target language. |
B. Demonstrate an awareness of elements of the students’ own culture. |
||
|
MLI.CCC3: The students compare basic elements of the target language to the English language. |
|||
|
A. Recognize similarities and differences in sound systems, writing systems, cognates, gender, and level appropriate idioms. |
B. Recognize basic sound distinctions and intonation patterns and their effect on communicating meaning. |
||
|
MLI.CCC4: The students demonstrate an awareness of current events in the target culture(s). |
|||
|
A. Give information regarding major current events of the target culture(s). |
B. Understand the impact of current events of the target culture(s). |
||
|
MLI.CCC5: The students identify situations and resources in which target language skills and cultural knowledge may be applied beyond the classroom setting, for recreational, educational, and occupational purposes. |
|||
|
A. Identify examples of the target language and the culture(s) studied that are evident in and through media, entertainment, and technology. |
B. Identify resources, such as individuals and organizations accessible through the community or the Internet, that provide basic cultural information about the culture(s) studied. |
||
- Details
- Category: Curriculum Standards
- Hits: 4705
|
COMMUNICATION – INTERPERSONAL MODE (IP) |
|||
|
MLI.IP1: The students exchange simple spoken and written information in the target language, utilizing cultural references where appropriate. |
|||
|
A. Use basic greetings, farewells, and expressions of courtesy, in both oral and written forms B. Express likes, dislikes, emotions, agreement and disagreement. C. Make simple requests. D. Ask for clarification. E. Give simple descriptions. |
F. Comprehend basic directions. G. Ask questions and provide responses based on topics such as self, family, school, etc. H. Use sequenced information, such as the alphabet, days of the week, months, seasons, and numbers 0 to 100 in context. |
||
|
MLI.IP2: The students demonstrate skills necessary to sustain brief oral and written exchanges in the target language. |
|||
|
A. Initiate, participate in, and close a brief oral or written exchange. B. Use formal and informal forms of address. |
C. Demonstrate Novice-Mid proficiency in oral and written exchanges with respect to proper pronunciation, intonation, and writing mechanics. |
||
|
|
|||
|
COMMUNICATION – INTERPRETIVE MODE (INT) |
|||
|
MLI.INT1: The students demonstrate understanding of simple spoken and written language presented through a variety of media in the target language and based on topics such as self, family, school, etc. |
|||
|
A. Identify main ideas and some details when reading and listening. B. Comprehend simple, culturally authentic announcements, messages, and advertisements. |
C. Understand simple instructions, such as classroom procedures. D. Demonstrate Novice-Mid proficiency in listening and reading comprehension. |
||
|
MLI.INT2: The students interpret verbal and non-verbal cues to understand simple spoken and written messages in the target language. |
|||
|
A. Differentiate among statements, questions and exclamations. |
B. Recognize basic gestures, body language, and intonation that clarify a message. |
||
|
|
|||
|
COMMUNICATION - PRESENTATIONAL MODE (P) |
|||
|
MLI.P1: The students present information orally and in writing that contains a variety of vocabulary, phrases, and patterns. |
|||
|
A. Present information gathered from a variety of sources such as informal conversations, class presentations, interviews, readings, and media. B. Give basic information about self and others including school, family, activities, etc. |
C. Demonstrate Novice-Mid proficiency in oral and written presentations with respect to proper pronunciation, intonation, and writing mechanics. |
||
|
MLI.P2: The students present brief, rehearsed material in the target language, such as dialogues, skits, poetry, and songs. |
|||
|
A. Demonstrate Novice-Mid proficiency in pronunciation and intonation when presenting rehearsed material. |
B. Demonstrate comprehension of rehearsed material. |
||
|
|
|||
|
CULTURAL PERSPECTIVES, PRACTICES, AND PRODUCTS (CU) |
|||
|
MLI.CU1: The students develop an awareness of perspectives, practices, and products of the cultures where the target language is spoken. |
|||
|
A. Demonstrate knowledge of contributions of target culture(s) to civilization. B. Identify commonly held viewpoints of the cultures, such as those relating to time, education, and meals. |
C. Describe customs and traditions of the cultures such as greetings, celebrations and courtesies. |
||
|
CONNECTIONS |
COMPARISONS |
COMMUNITIES |
|
|
MLI.CCC1: The students use information acquired in the study of the target language and information acquired in other subject areas to reinforce one another. |
|||
|
A. Demonstrate knowledge of geographical locations and identify major countries, cities, and geographical features of the places where the target language is spoken. B. Apply previously learned skills from other subjects, when appropriate to demonstrate knowledge in the target language (e.g. using basic math skills). |
C. Identify examples of vocabulary, phrases, proverbs, and symbols from the target language that are used in other subjects. D. Relate content from other subject areas to topics discussed in the language class, such as the influence of explorers and settlers on various regions of the United States. |
||
|
MLC.CCC2: The students demonstrate an understanding of the significance of culture through comparisons between the culture(s) studied and the students’ own culture. |
|||
|
A. Compare patterns of behavior and interaction in the students’ own culture with those of the target language. |
B. Demonstrate an awareness of elements of the students’ own culture. |
||
|
MLI.CCC3: The students compare basic elements of the target language to the English language. |
|||
|
A. Recognize similarities and differences in sound systems, writing systems, cognates, gender, and level appropriate idioms. |
B. Recognize basic sound distinctions and intonation patterns and their effect on communicating meaning. |
||
|
MLI.CCC4: The students demonstrate an awareness of current events in the target culture(s). |
|||
|
A. Give information regarding major current events of the target culture(s). |
B. Understand the impact of current events of the target culture(s). |
||
|
MLI.CCC5: The students identify situations and resources in which target language skills and cultural knowledge may be applied beyond the classroom setting, for recreational, educational, and occupational purposes. |
|||
|
A. Identify examples of the target language and the culture(s) studied that are evident in and through media, entertainment, and technology. |
B. Identify resources, such as individuals and organizations accessible through the community or the Internet, that provide basic cultural information about the culture(s) studied. |
||
- Details
- Category: Curriculum Standards
- Hits: 1935
|
COMMUNICATION – INTERPERSONAL MODE (IP) |
|||
|
MLI.IP1: The students exchange simple spoken and written information in the target language, utilizing cultural references where appropriate. |
|||
|
A. Use basic greetings, farewells, and expressions of courtesy, in both oral and written forms B. Express likes, dislikes, emotions, agreement and disagreement. C. Make simple requests. D. Ask for clarification. E. Give simple descriptions. |
F. Comprehend basic directions. G. Ask questions and provide responses based on topics such as self, family, school, etc. H. Use sequenced information, such as the alphabet, days of the week, months, seasons, and numbers 0 to 100 in context. |
||
|
MLI.IP2: The students demonstrate skills necessary to sustain brief oral and written exchanges in the target language. |
|||
|
A. Initiate, participate in, and close a brief oral or written exchange. B. Use formal and informal forms of address. |
C. Demonstrate Novice-Mid proficiency in oral and written exchanges with respect to proper pronunciation, intonation, and writing mechanics. |
||
|
|
|||
|
COMMUNICATION – INTERPRETIVE MODE (INT) |
|||
|
MLI.INT1: The students demonstrate understanding of simple spoken and written language presented through a variety of media in the target language and based on topics such as self, family, school, etc. |
|||
|
A. Identify main ideas and some details when reading and listening. B. Comprehend simple, culturally authentic announcements, messages, and advertisements. |
C. Understand simple instructions, such as classroom procedures. D. Demonstrate Novice-Mid proficiency in listening and reading comprehension. |
||
|
MLI.INT2: The students interpret verbal and non-verbal cues to understand simple spoken and written messages in the target language. |
|||
|
A. Differentiate among statements, questions and exclamations. |
B. Recognize basic gestures, body language, and intonation that clarify a message. |
||
|
|
|||
|
COMMUNICATION - PRESENTATIONAL MODE (P) |
|||
|
MLI.P1: The students present information orally and in writing that contains a variety of vocabulary, phrases, and patterns. |
|||
|
A. Present information gathered from a variety of sources such as informal conversations, class presentations, interviews, readings, and media. B. Give basic information about self and others including school, family, activities, etc. |
C. Demonstrate Novice-Mid proficiency in oral and written presentations with respect to proper pronunciation, intonation, and writing mechanics. |
||
|
MLI.P2: The students present brief, rehearsed material in the target language, such as dialogues, skits, poetry, and songs. |
|||
|
A. Demonstrate Novice-Mid proficiency in pronunciation and intonation when presenting rehearsed material. |
B. Demonstrate comprehension of rehearsed material. |
||
|
|
|||
|
CULTURAL PERSPECTIVES, PRACTICES, AND PRODUCTS (CU) |
|||
|
MLI.CU1: The students develop an awareness of perspectives, practices, and products of the cultures where the target language is spoken. |
|||
|
A. Demonstrate knowledge of contributions of target culture(s) to civilization. B. Identify commonly held viewpoints of the cultures, such as those relating to time, education, and meals. |
C. Describe customs and traditions of the cultures such as greetings, celebrations and courtesies. |
||
|
CONNECTIONS |
COMPARISONS |
COMMUNITIES |
|
|
MLI.CCC1: The students use information acquired in the study of the target language and information acquired in other subject areas to reinforce one another. |
|||
|
A. Demonstrate knowledge of geographical locations and identify major countries, cities, and geographical features of the places where the target language is spoken. B. Apply previously learned skills from other subjects, when appropriate to demonstrate knowledge in the target language (e.g. using basic math skills). |
C. Identify examples of vocabulary, phrases, proverbs, and symbols from the target language that are used in other subjects. D. Relate content from other subject areas to topics discussed in the language class, such as the influence of explorers and settlers on various regions of the United States. |
||
|
MLC.CCC2: The students demonstrate an understanding of the significance of culture through comparisons between the culture(s) studied and the students’ own culture. |
|||
|
A. Compare patterns of behavior and interaction in the students’ own culture with those of the target language. |
B. Demonstrate an awareness of elements of the students’ own culture. |
||
|
MLI.CCC3: The students compare basic elements of the target language to the English language. |
|||
|
A. Recognize similarities and differences in sound systems, writing systems, cognates, gender, and level appropriate idioms. |
B. Recognize basic sound distinctions and intonation patterns and their effect on communicating meaning. |
||
|
MLI.CCC4: The students demonstrate an awareness of current events in the target culture(s). |
|||
|
A. Give information regarding major current events of the target culture(s). |
B. Understand the impact of current events of the target culture(s). |
||
|
MLI.CCC5: The students identify situations and resources in which target language skills and cultural knowledge may be applied beyond the classroom setting, for recreational, educational, and occupational purposes. |
|||
|
A. Identify examples of the target language and the culture(s) studied that are evident in and through media, entertainment, and technology. |
B. Identify resources, such as individuals and organizations accessible through the community or the Internet, that provide basic cultural information about the culture(s) studied. |
||
- Details
- Category: Curriculum Standards
- Hits: 1964
|
COMMUNICATION – INTERPERSONAL MODE (IP) |
|||
|
MLI.IP1: The students exchange simple spoken and written information in the target language, utilizing cultural references where appropriate. |
|||
|
A. Use basic greetings, farewells, and expressions of courtesy, in both oral and written forms B. Express likes, dislikes, emotions, agreement and disagreement. C. Make simple requests. D. Ask for clarification. E. Give simple descriptions. |
F. Comprehend basic directions. G. Ask questions and provide responses based on topics such as self, family, school, etc. H. Use sequenced information, such as the alphabet, days of the week, months, seasons, and numbers 0 to 100 in context. |
||
|
MLI.IP2: The students demonstrate skills necessary to sustain brief oral and written exchanges in the target language. |
|||
|
A. Initiate, participate in, and close a brief oral or written exchange. B. Use formal and informal forms of address. |
C. Demonstrate Novice-Mid proficiency in oral and written exchanges with respect to proper pronunciation, intonation, and writing mechanics. |
||
|
|
|||
|
COMMUNICATION – INTERPRETIVE MODE (INT) |
|||
|
MLI.INT1: The students demonstrate understanding of simple spoken and written language presented through a variety of media in the target language and based on topics such as self, family, school, etc. |
|||
|
A. Identify main ideas and some details when reading and listening. B. Comprehend simple, culturally authentic announcements, messages, and advertisements. |
C. Understand simple instructions, such as classroom procedures. D. Demonstrate Novice-Mid proficiency in listening and reading comprehension. |
||
|
MLI.INT2: The students interpret verbal and non-verbal cues to understand simple spoken and written messages in the target language. |
|||
|
A. Differentiate among statements, questions and exclamations. |
B. Recognize basic gestures, body language, and intonation that clarify a message. |
||
|
|
|||
|
COMMUNICATION - PRESENTATIONAL MODE (P) |
|||
|
MLI.P1: The students present information orally and in writing that contains a variety of vocabulary, phrases, and patterns. |
|||
|
A. Present information gathered from a variety of sources such as informal conversations, class presentations, interviews, readings, and media. B. Give basic information about self and others including school, family, activities, etc. |
C. Demonstrate Novice-Mid proficiency in oral and written presentations with respect to proper pronunciation, intonation, and writing mechanics. |
||
|
MLI.P2: The students present brief, rehearsed material in the target language, such as dialogues, skits, poetry, and songs. |
|||
|
A. Demonstrate Novice-Mid proficiency in pronunciation and intonation when presenting rehearsed material. |
B. Demonstrate comprehension of rehearsed material. |
||
|
|
|||
|
CULTURAL PERSPECTIVES, PRACTICES, AND PRODUCTS (CU) |
|||
|
MLI.CU1: The students develop an awareness of perspectives, practices, and products of the cultures where the target language is spoken. |
|||
|
A. Demonstrate knowledge of contributions of target culture(s) to civilization. B. Identify commonly held viewpoints of the cultures, such as those relating to time, education, and meals. |
C. Describe customs and traditions of the cultures such as greetings, celebrations and courtesies. |
||
|
CONNECTIONS |
COMPARISONS |
COMMUNITIES |
|
|
MLI.CCC1: The students use information acquired in the study of the target language and information acquired in other subject areas to reinforce one another. |
|||
|
A. Demonstrate knowledge of geographical locations and identify major countries, cities, and geographical features of the places where the target language is spoken. B. Apply previously learned skills from other subjects, when appropriate to demonstrate knowledge in the target language (e.g. using basic math skills). |
C. Identify examples of vocabulary, phrases, proverbs, and symbols from the target language that are used in other subjects. D. Relate content from other subject areas to topics discussed in the language class, such as the influence of explorers and settlers on various regions of the United States. |
||
|
MLC.CCC2: The students demonstrate an understanding of the significance of culture through comparisons between the culture(s) studied and the students’ own culture. |
|||
|
A. Compare patterns of behavior and interaction in the students’ own culture with those of the target language. |
B. Demonstrate an awareness of elements of the students’ own culture. |
||
|
MLI.CCC3: The students compare basic elements of the target language to the English language. |
|||
|
A. Recognize similarities and differences in sound systems, writing systems, cognates, gender, and level appropriate idioms. |
B. Recognize basic sound distinctions and intonation patterns and their effect on communicating meaning. |
||
|
MLI.CCC4: The students demonstrate an awareness of current events in the target culture(s). |
|||
|
A. Give information regarding major current events of the target culture(s). |
B. Understand the impact of current events of the target culture(s). |
||
|
MLI.CCC5: The students identify situations and resources in which target language skills and cultural knowledge may be applied beyond the classroom setting, for recreational, educational, and occupational purposes. |
|||
|
A. Identify examples of the target language and the culture(s) studied that are evident in and through media, entertainment, and technology. |
B. Identify resources, such as individuals and organizations accessible through the community or the Internet, that provide basic cultural information about the culture(s) studied. |
||
- Details
- Category: Curriculum Standards
- Hits: 2338
 The International Society for Technology in Education - ISTE® is a worldwide nonprofit organization of educators and education leaders committed to empowering connected learners in a connected world. The family of ISTE Standards works in concert to support students, educators and leaders with clear guidelines for the skills, knowledge and approaches they need to succeed in the digital age.
The International Society for Technology in Education - ISTE® is a worldwide nonprofit organization of educators and education leaders committed to empowering connected learners in a connected world. The family of ISTE Standards works in concert to support students, educators and leaders with clear guidelines for the skills, knowledge and approaches they need to succeed in the digital age.
Click on the links below to download the standards for each group:
Content from http://www.iste.org/
- Details
- Category: Curriculum Standards
- Hits: 7873
The language proficiency targets indicate what students are expected to do with the language at the end of each course in terms of producing language (speaking and writing), understanding language (listening and reading), and interacting with others in the language. Proficiency targets for each language are based on the American Council on the Teaching of Foreign Languages (ACTFL) Proficiency Guidelines.
Click on each of the headings for details on the target skills for each level.
|
Level |
||||||
| K-5th Grade DLI - Bilingual |
Intermediate Mid |
Intermediate Mid |
Intermediate Mid |
Intermediate High |
Intermediate Mid |
Intermediate (-) |
|
6th Grade |
Novice Low |
Novice Low |
Novice Low |
Novice Low |
Novice Mid |
Novice |
|
7th Grade |
Novice Mid |
Novice Mid |
Novice Mid |
Novice Mid |
Novice High |
Novice |
|
Level I |
Novice High |
Novice High |
Novice High |
Novice High |
Intermediate Low |
Novice |
|
Level II |
Intermediate Low |
Intermediate Low |
Intermediate Low |
Intermediate Low |
Intermediate Mid (-) |
Intermediate (-) |
|
Level III |
Intermediate Mid (-) |
Intermediate Mid (-) |
Intermediate Mid (-) |
Intermediate Mid (-) |
Intermediate Mid |
Intermediate (-) |
|
Level IV |
Intermediate Mid |
Intermediate Mid |
Intermediate Mid |
Intermediate Mid |
Intermediate |
Intermediate |
|
Level V - VIII |
Intermediate High (-) to Advanced Low |
Intermediate High (-) to Advanced Low |
Intermediate High (-) to Advanced Low |
Intermediate High (-) to Advanced Low |
Intermediate High to Advanced Low |
Advanced |
|
Native Speakers I |
Intermediate High (-) |
Intermediate High (-) |
Intermediate Low |
Intermediate High |
Intermediate Low |
Intermediate (-) |
|
Native Speakers II |
Advanced Low (-) | Advanced Low (-) | Intermediate High (-) |
Advanced Low (-) | Intermediate High (-) |
Intermediate |
|
Native Speakers III |
Advanced Low | Advanced Low | Intermediate High |
Advanced Low | Intermediate High |
Advanced (-) |
Learn more about ACTFL's Language Proficiency Guidelines and the NCSSFL-ACTFL Global CAN-DO Benchmark Statements.
- Details
- Category: Language Proficiency
- Hits: 8746
The language proficiency targets indicate what students are expected to do with the language at the end of each course in terms of producing language (speaking and writing), understanding language (listening and reading), and interacting with others in the language. Proficiency targets for each language are based on the American Council on the Teaching of Foreign Languages (ACTFL) Proficiency Guidelines.
Click on each of the headings for details on the target skills for each level.
|
Level |
||||||
|
7th Grade |
Novice Mid |
Novice Mid |
Novice Mid |
Novice Mid |
Novice High |
Novice |
|
Level I |
Novice High |
Novice High |
Novice High |
Novice High |
Intermediate Low |
Novice |
|
Level II |
Intermediate Low |
Intermediate Low |
Intermediate Low |
Intermediate Low |
Intermediate Mid (-) |
Intermediate (-) |
|
Level III |
Intermediate Mid (-) |
Intermediate Mid (-) |
Intermediate Mid (-) |
Intermediate Mid (-) |
Intermediate Mid |
Intermediate (-) |
|
Level IV |
Intermediate Mid |
Intermediate Mid |
Intermediate Mid |
Intermediate Mid |
Intermediate |
Intermediate |
|
Level V - VIII |
Intermediate High (-) to Advanced Low |
Intermediate High (-) to Advanced Low |
Intermediate High (-) to Advanced Low |
Intermediate High (-) to Advanced Low |
Intermediate High to Advanced Low |
Advanced |
Learn more about ACTFL's Language Proficiency Guidelines and the NCSSFL-ACTFL Global CAN-DO Benchmark Statements.
- Details
- Category: Language Proficiency
- Hits: 5881
Communication
To share or exchange information, news, or ideas effectively in more than one language in order to function in a variety of situations and for multiple purposes.
 Interpretive Communication
Interpretive Communication
Learners understand, interpret, and analyze what is heard, read, or viewed on a variety of topics.
| Click the icons below to download the Interpretive Communication Self-Assessment Checklists. | Click the icons below to see the proficiency guidelines for each level. | ||
| Interpretive Listening |
Novice |
Intermediate | Advanced |
 |
 |
||
| Interpretive Reading | |||
 |
 |
 |
|
American Council of Teaching of Foreign Languages (ACTFL)
- Details
- Category: Language Proficiency
- Hits: 3722
Subcategories
Arabic
Arabic Language Program
The Cobb County Arabic program offers the following courses:
- Levels I-IV
*Not all schools offer all the course levels or languages, please check with your local school for a list of current course offerings.
Why should you learn Arabic?
Visit the Lead with Languages site and learn more about the benefits of learning Arabic and other languages.
Click HERE to learn more about the languages offered at Cobb County Schools.
Chinese
Chinese Language Program
The Cobb County Chinese program offers the following courses:
- Levels I-V
- AP Chinese Language and Culture
*Not all schools offer all the course levels or languages, please check with your local school for a list of current course offerings.
Why should you learn Chinese?
Visit the Lead with Languages site and learn more about the benefits of learning Chinese and other languages.
Click HERE to learn more about the languages offered at Cobb County Schools.
French
French Language Program
Visit the Lead with Languages site and learn more about the benefits of learning French and other languages.
Click HERE to learn more about the languages offered at Cobb County Schools.
The Cobb County French program offers the following courses:
- Levels I-VIII
- AP Language & Culture
*Not all schools offer all the course levels or languages, please check with your local school for a list of current course offerings.
** Teacher Log-in is required to access some of the resources below:
| Course Profile |
Proficiency Targets |
Instructional Resources |
Click on the links below for additional resources:
- Teacher Resources (log in required)
- Student Textbook Resources
- Online resources
German
German Language Program
The Cobb County German program offers the following courses:
- Levels I-VI
- AP German Language and Culture
*Not all schools offer all the course levels or languages, please check with your local school for a list of current course offerings.
Why should you learn German?
Visit the Lead with Languages site and learn more about the benefits of learning German and other languages.
Click HERE to learn more about the languages offered at Cobb County Schools.
** Teacher Log-in is required to access some of the resources below:
| Course Profile |
Proficiency Targets |
Instructional Resources |
Japanese
Japanese Language Program
The Cobb County Japanese program offers the following courses:
- Levels I-V
*Not all schools offer all the course levels or languages, please check with your local school for a list of current course offerings.
Why should you learn Japanese?
Visit the Lead with Languages site and learn more about the benefits of learning Japanese and other languages.
Click HERE to learn more about the languages offered at Cobb County Schools.
Click on the links below for additional resources: (Coming soon)
- Teacher Resources (log in required)
- Student Textbook Resources
- Online resources
Latin
Latin Language Program
The Cobb County Latin program offers the following courses:
- Levels I-VI
- AP Latin Language
*Not all schools offer all the course levels or languages, please check with your local school for a list of current course offerings.
Why should you learn Latin?
Visit the Lead with Languages site and learn more about the benefits of learning Latin and other languages.
Click HERE to learn more about the languages offered at Cobb County Schools.
Click on the links below for additional resources: (Coming soon)
- Teacher Resources (log in required)
- Student Textbook Resources
- Online resources
Portuguese
Portuguese Language Program
The Cobb County Portuguese program is currently offered at our Magnet School for International Studies at North Cobb High School. We offer the following courses:
- Levels I-III
*Not all schools offer all the course levels or languages, please check with your local school for a list of current course offerings.
Why should you learn Portuguese?
Visit the Lead with Languages site and learn more about the benefits of learning Portuguese and other languages.
Click HERE to learn more about the languages offered at Cobb County Schools.
Spanish
Spanish Language Program
The Cobb County Spanish program offers the following courses
- Levels I - VIII
- AP Language & Culture
- AP Literature & Culture
- Spanish for native speakers Levels I - II
*Not all schools offer all the course levels or languages, please check with your local school for a list of current course offerings.
** Teacher Log-in is required to access some of the resources below:
| Course Profile |
Proficiency Targets |
Instructional Resources |
Why should you learn Spanish?
Visit the Lead with Languages site and learn more about the benefits of learning Spanish and other languages.
Click HERE to learn more about the languages offered at Cobb County Schools.
American Sign Language
American Sign Language Program
The Cobb County ASL program offers the following courses:
- Levels I-IV
*Not all schools offer all the course levels or languages, please check with your local school for a list of current course offerings.
Why should you learn American Sign Language?
Visit the Lead with Languages site and learn more about the benefits of learning American Sign Language and other languages.
Click HERE to learn more about the languages offered at Cobb County Schools.
Dual Language Immersion
Cobb County Schools Bilingual Programs
Dual Language Immersion
Dual Language Immersion is a way to learn academic content while acquiring another language at the same time. Starting the 2015-2016 academic year, Cobb County students have the opportunity to participate in the Dual Language Immersion Program (DLI). The goals of the program are for the students to develop literacy skills in both English and the target language while attaining a high level of academic achievement that is at or above their grade level in all content areas and to develop a world cultural sensitivity. Each school/community chooses the immersion language for its school.
What schools and grade levels are currently offering the DLI program?
Dual Language Immersion programs provide students with academic instruction in two languages. In addition to gaining grade-level content-area knowledge and skills, students develop higher levels of language competency.
The list below indicates the available bilingual programs available in Cobb at the Elementary and High School levels.
Elementary Schools (K-5)
DLI programs at the elementary level will continue to grow one grade level at a time every school year as students move from Kindergarten through 5th grade. Please see the chart below for a list of current schools offering the Dual Immersion program, the language of the program, and the grade levels available for each academic year.
School Year 2022 - 2023
| School | Grades |
| 6 - 7 | |
| 1 - 3 | |
| K - 5 | |
| 1 - 5 | |
| 6 | |
| 1 - 5 | |
| K - 5 | |
| K - 5 | |
| 1 - 5 | |
| 2 - 4 | |
| K - 5 | |
| K - 5 |
How does it look in the classroom?
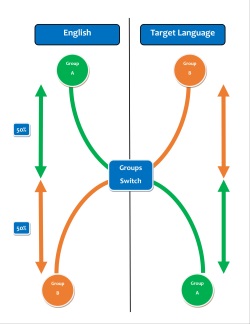 Elementary: Instruction is divided between two high-quality, creative classrooms: one English and one immersion (target language) with fifty percent of the academic day taught in English and fifty percent of the academic day taught in the target language. Students enjoy the advantage of two caring, highly qualified teachers. The English-speaking teacher uses half of the instructional day to teach English Language Arts, literacy, and content area support. The immersion teacher uses the other half of the day to teach math, science, social studies, and target language literacy. Teachers are trained in the use of instructional strategies that promote language learning and academic development.
Elementary: Instruction is divided between two high-quality, creative classrooms: one English and one immersion (target language) with fifty percent of the academic day taught in English and fifty percent of the academic day taught in the target language. Students enjoy the advantage of two caring, highly qualified teachers. The English-speaking teacher uses half of the instructional day to teach English Language Arts, literacy, and content area support. The immersion teacher uses the other half of the day to teach math, science, social studies, and target language literacy. Teachers are trained in the use of instructional strategies that promote language learning and academic development.
What skills/content do the students learn in the DLI program?
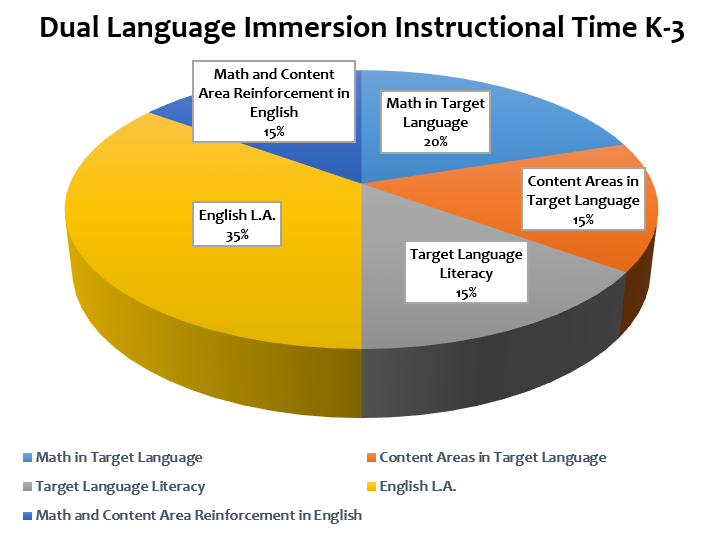
Students in the Dual Immersion Program learn the concepts and skills for the various subject areas at the same time that they develop the ability to read, write, speak, and listen in another language. Students learn the same concepts and skills for the various subject areas as their grade-level peers at the same time that they develop the ability to read, write, speak, and listen in another language. Students receive math, science, and social studies instruction in a target language, such as Spanish, French, or Chinese.
What are the benefits of Dual Language Immersion?
Language Skills: Students achieve high proficiency in the immersion language. Immersion students become bilingual and biliterate.
Improved Performance on Standardized Tests: Immersion students perform as well as or better than non-immersion students on standardized tests of English and math administered in English.
Enhanced Cognitive Skills: Immersion students typically develop greater cognitive flexibility, demonstrating increased attention control, better memory, and superior problem-solving skills as well as an enhanced understanding of their primary language.
Increased Cultural Sensitivity: Immersion students are more aware of and show more positive attitudes towards other cultures and an appreciation of other people.
Long Term Benefits: Immersion students are better prepared for the global community and job markets where a second language is an asset.
Language Academies - High School (9-12)
DLI programs at the high school level will continue to grow one grade level at a time every school year as students move from 9th through 12th grade. Please see the chart below for a list of current schools offering the Dual Immersion program, the language of the program, and the grade levels available for each academic year.
| School | Grades |
| 9 - 12 | |
 |
9 - 12 |
a
Curriculum Elements
Language Proficiency
Cobb County World Language Program courses are designed to assist the students' development of language and intercultural skills. Each course has set learning targets based on ACTFL's language proficiency standards and NCSSFL-ACTFL Can Do Statements. ACTFL standards goal areas are: Communication, Cultures, Connections, Comparisons, and Communities.
Communication
This is the main area of the standards and in which we based a great part of our course program. There are three modes within the communication standards, Interpersonal, Presentational, and Interpretive. Use the links below to learn more about the language domains and sublevels for each mode.
| MODES | |||||
| LEVELS | |||||
| Novice |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Intermediate |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Advanced |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Culture
The study of culture and language is strongly interconnected. Students use the language to investigate and interact properly with the practices, perspectives, and products of the various cultures.
| LEVELS | |||
| Novice |  |
 |
 |
| Intermediate |  |
 |
 |
| Advanced |  |
 |
 |
For more information and resources about language proficiency go to the American Council for Teachers of Foreign Languages (ACTFL) at: https://www.actfl.org/
Page 5 of 8